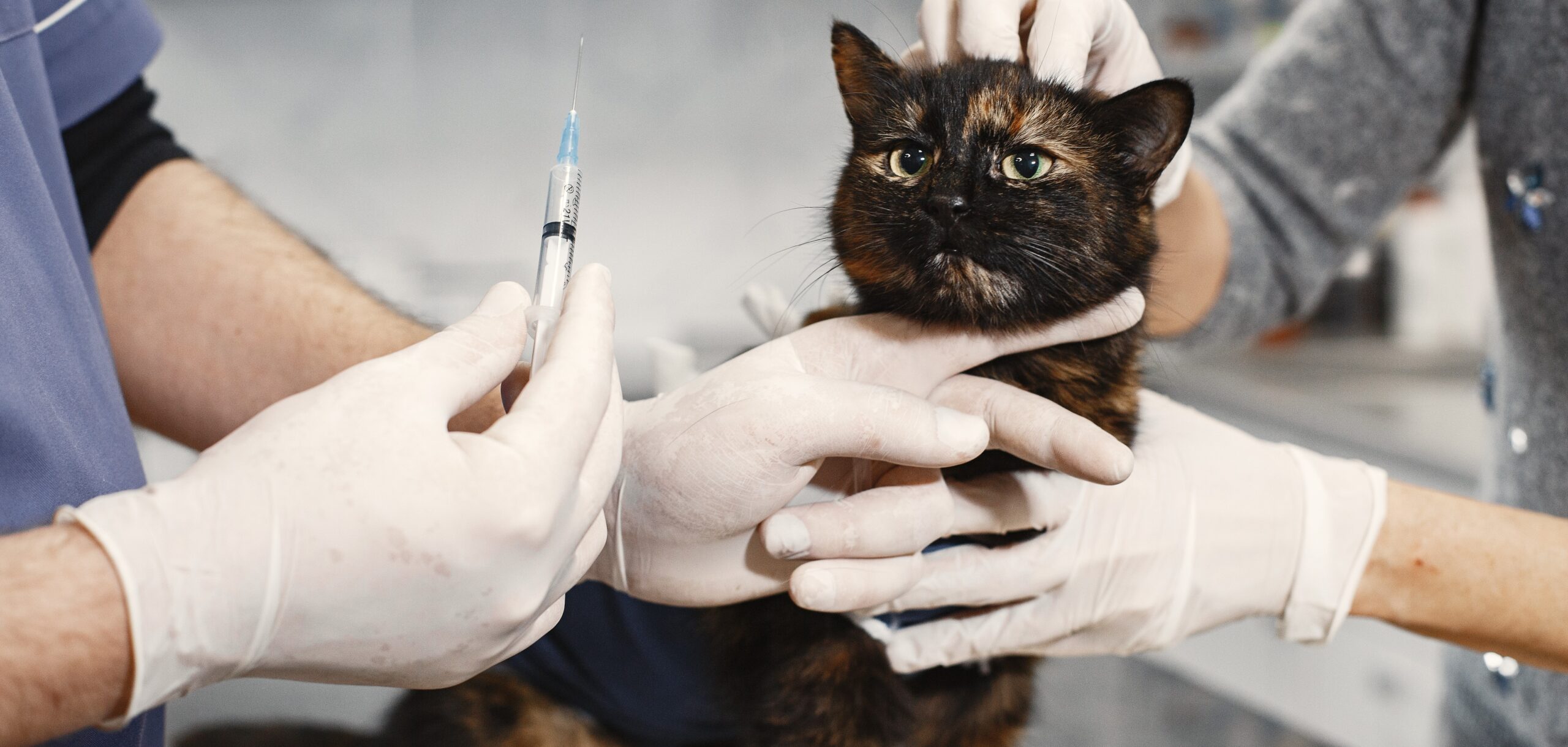
Booster Shots for Pets
As pet owners, we want the best for our furry friends, and that includes keeping them healthy and protected against diseases. One way to do this is by getting booster shots for pets. Booster shots are additional vaccinations given after the initial round of shots to keep your pet’s immune system strong and able to fight off infections. In this article, we’ll explore the benefits of booster shots for pets and why they’re important.
What are Booster Shots for Pets?
Booster shots are follow-up vaccinations given to pets to boost their immunity against certain diseases. These shots are typically given annually or every three years, depending on the vaccine and the pet’s age and health. The timing of booster shots varies depending on the type of vaccine, so it’s important to consult with your veterinarian to determine the appropriate schedule for your pet.
Why are Booster Shots Important for Pets?
Booster shots are important for several reasons. First, they help protect your pet against infectious diseases. Vaccines work by stimulating your pet’s immune system to produce antibodies that can fight off specific viruses or bacteria. Booster shots help reinforce your pet’s immunity to these diseases, making it less likely for them to get sick.
Secondly, booster shots are important for preventing the spread of diseases. Some vaccines, such as the rabies vaccine, are required by law in many states to prevent the spread of the disease to humans and other animals. Keeping your pet up to date on their booster shots is an important part of being a responsible pet owner.
Lastly, booster shots can save you money in the long run. Treating a sick pet can be expensive, and some diseases can be fatal. By keeping your pet’s immunity strong through regular booster shots, you can avoid costly veterinary bills and keep your pet healthy and happy.
Common Booster Shots for Pets
There are several common booster shots for pets, including:
- Rabies: The rabies vaccine is required by law in many states and is typically given every one to three years, depending on the vaccine and the pet’s age and health.
- Distemper: The distemper vaccine is a combination vaccine that protects against several diseases, including distemper, adenovirus, parainfluenza, and parvovirus. It’s typically given annually.
- Bordetella: The bordetella vaccine, also known as the “kennel cough” vaccine, protects against a bacterial infection that can cause coughing, sneezing, and other respiratory symptoms. It’s typically given annually or every six months, depending on the vaccine.
- Leptospirosis: The leptospirosis vaccine protects against a bacterial infection that can cause liver and kidney damage. It’s typically given annually.
Conclusion:
Booster shots for pets are an important part of keeping your furry friend healthy and protected against infectious diseases. They help boost your pet’s immunity and prevent the spread of diseases, and they can save you money in the long run by avoiding costly veterinary bills. Talk to your veterinarian to determine the appropriate schedule for your pet’s booster shots, and make sure to keep them up to date to ensure their continued health and happiness.
You May be Interested in…
Vaccines Schedules for Puppies and Kittens
Vaccine Schedules for Adult Dogs and Cats