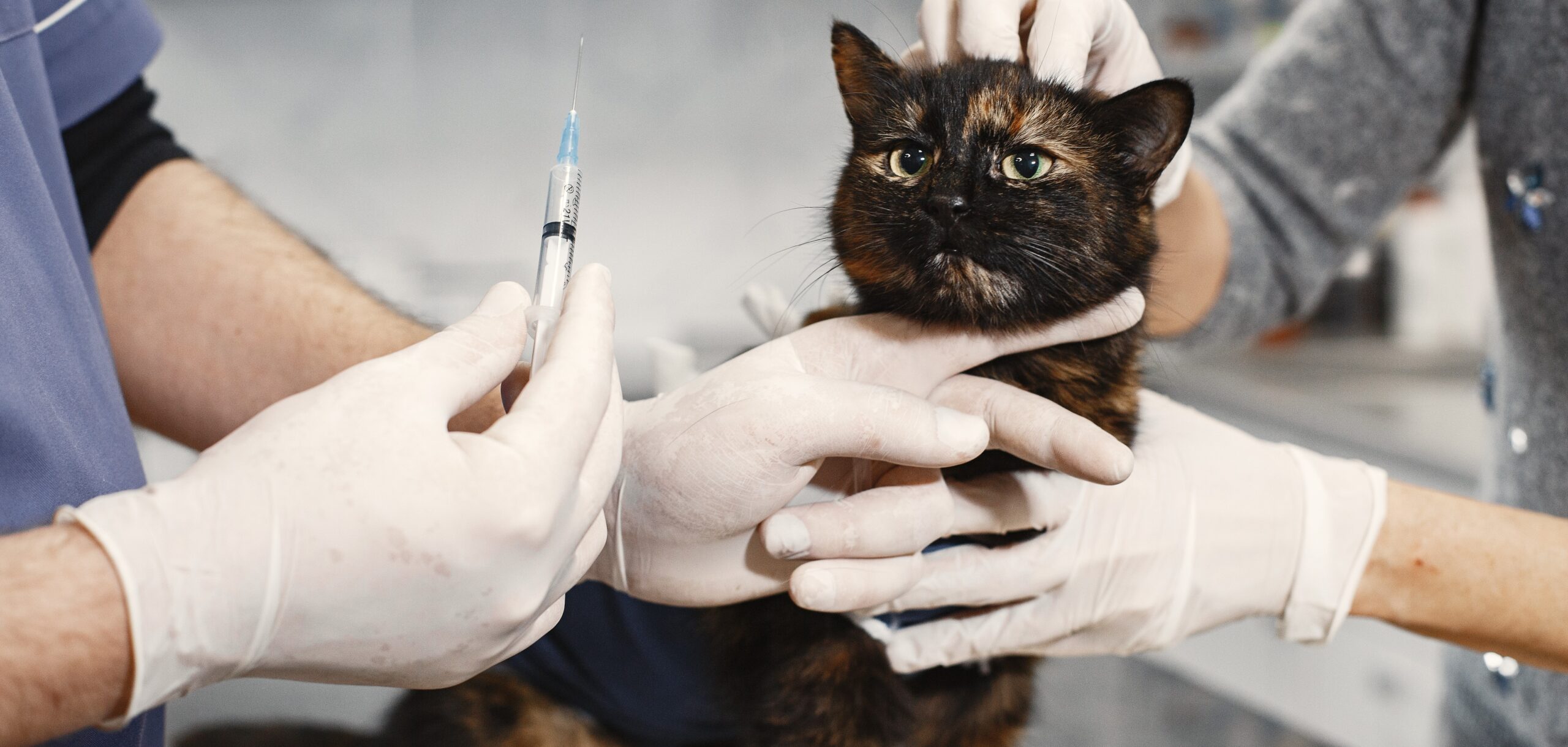
Vaccines Schedules for Puppies and Kittens
As a new pet owner, one of the most important things you can do for your furry friend’s health is to make sure they are properly vaccinated. Vaccines protect your pet from serious, and sometimes deadly, diseases that can be easily spread. Vaccines work by stimulating your pet’s immune system to produce antibodies that fight off infections. So it is important to give attention on the vaccines schedules for puppies and kittens
In this article we will discuss all you need to know about Vaccines Schedules for Puppies and Kittens in core detail.
Puppy Vaccination Schedule:
Puppies are typically vaccinated against a variety of diseases, including distemper, parvovirus, hepatitis, and rabies. Puppies receive their first round of vaccinations between 6-8 weeks old, followed by booster shots every 3-4 weeks until they are 16-20 weeks old. After their initial round of vaccinations, puppies need to receive annual booster shots to maintain immunity.
The core vaccines that all puppies should receive are:
- Distemper: A highly contagious virus that attacks the respiratory, gastrointestinal, and nervous systems of dogs. Symptoms include fever, coughing, and vomiting.
- Parvovirus: A virus that attacks the intestinal tract, leading to severe diarrhea, vomiting, and dehydration. Parvo can be deadly, especially in puppies.
- Hepatitis: A viral infection that affects the liver, kidneys, spleen, lungs, and eyes. Symptoms include fever, lethargy, and abdominal pain.
- Rabies: A fatal viral disease that attacks the nervous system of animals, including humans. Rabies is transmitted through the saliva of infected animals, and is a public health concern.
Kitten Vaccination Schedule:
Kittens are also susceptible to a variety of diseases, including feline herpesvirus, feline calicivirus, panleukopenia, and rabies. Kittens receive their first round of vaccinations at 6-8 weeks old, followed by booster shots every 3-4 weeks until they are 16-20 weeks old. After their initial round of vaccinations, kittens need to receive annual booster shots to maintain immunity.
The core vaccines that all kittens should receive are:
- Feline herpesvirus and feline calicivirus: These are the two most common causes of upper respiratory infections in cats. Symptoms include sneezing, runny nose, and eye discharge.
- Panleukopenia: Also known as feline distemper, this is a highly contagious viral disease that attacks the digestive and nervous systems of cats. Symptoms include vomiting, diarrhea, and dehydration.
- Rabies: A fatal viral disease that attacks the nervous system of animals, including humans. Rabies is transmitted through the saliva of infected animals, and is a public health concern.
It’s important to note that your pet’s vaccination schedule may vary depending on their age, breed, and lifestyle. Some pets may require additional vaccines based on their environment or travel plans. Be sure to discuss your pet’s vaccination schedule with your veterinarian to ensure they are fully protected.
In conclusion, vaccines are an essential part of your pet’s health and wellbeing. By following the appropriate vaccination schedule, you can help protect your pet from potentially deadly diseases. Remember to work closely with your veterinarian to determine the best vaccination plan for your furry friend.
You May be Interested in…
Importance of Pet Vaccination: A Comprehensive Guide
Discover all You Need to Know about Your Pet Health and Wellness